Staying ahead in today’s digital race isn’t just an option—it’s a necessity. The key? Modernizing your applications to keep up with innovation, efficiency, and ever-changing market demands. While legacy systems were once efficient, they often become bottlenecks that hinder operational efficiency, agility, and innovation over time. Therefore, a well-planned Application Modernization Strategy is essential for organizations looking to upgrade their outdated applications and align them with current technological trends.
This blog delves deep into Application Modernization Strategies, with a focus on the 7 R’s of Application Modernization, providing actionable insights tailored for MSMEs and niche industry sectors. By understanding these strategies, businesses can transition smoothly from legacy systems to modern, scalable, and cost-effective solutions.
Understanding Application Modernization
Application modernization refers to the process of upgrading and transforming legacy applications to integrate with modern infrastructure, technologies, and business needs. As a result, businesses can re-architect, re-platform, or re-host applications to enhance their performance, scalability, and security while optimizing costs.
For MSMEs, Legacy Application Modernization is not just an option—it is a necessity. Outdated applications can limit growth, reduce efficiency, and increase maintenance costs. Consequently, modernizing these systems allows businesses to improve agility, enhance customer experiences, and stay ahead of the competition.
Why Modernize Legacy Applications?
Modernizing legacy applications is crucial for organizations that want to eliminate inefficiencies and leverage modern technologies such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and automation. In fact, a well-executed Application Modernization Strategy comes with multiple advantages, such as:
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Streamlining business processes by removing outdated dependencies.
- Enhanced User Experience: Offering seamless, intuitive, and high-performing applications.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Lowering costs associated with maintaining and supporting outdated software.
- Increased Agility and Scalability: Quickly adapting to market changes and scaling resources as needed.
- Strengthened Security Measures: Protecting business-critical data with modern security protocols.
The 7 R’s of Application Modernization: A Comprehensive Approach
To effectively modernize legacy applications, businesses must assess their current systems and choose the right modernization approach. That’s where the 7 R’s of Application Modernization come into play, providing a structured framework for decision-making:
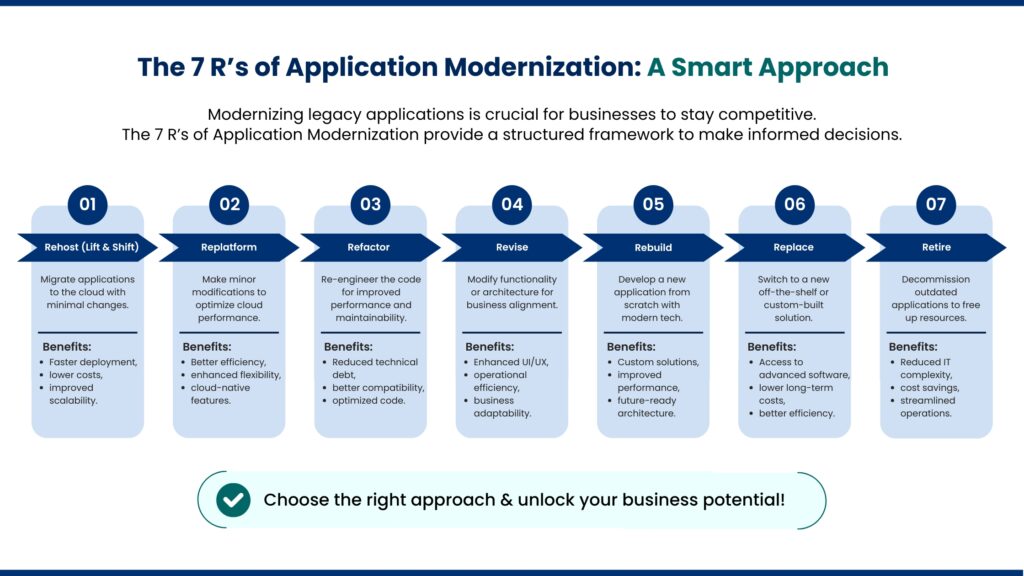
1. Rehost
Rehosting, commonly known as “lift-and-shift,” involves migrating applications from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud with minimal changes. This strategy is ideal for businesses looking for a quick transition with minimal disruption.
Benefits:
- Faster deployment with minimal downtime
- Reduced infrastructure costs
- Immediate access to cloud benefits like scalability and reliability
2. Replatform
Replatforming requires minor modifications to an application to optimize it for a new platform, such as the cloud. Unlike rehosting, replatforming allows organizations to leverage cloud-native features without a complete overhaul.
Benefits:
- Improved performance and efficiency
- Better resource utilization in cloud environments
- Enhanced scalability and flexibility
3. Refactor
Refactoring involves re-engineering the application’s codebase to improve performance, maintainability, and alignment with modern standards without altering its core functionality.
Benefits:
- Enhanced code efficiency and maintainability
- Reduced technical debt
- Improved performance and compatibility with modern technologies
4. Revise
Revision focuses on modifying an application’s functionality or architecture to better align with business goals. This approach is often used for applications that require significant updates but do not need a complete rebuild.
Benefits:
- Modernized UI/UX for better customer experience
- Enhanced business functionality
- Improved operational efficiency
5. Rebuild
Rebuilding an application means developing it from scratch using modern technologies while retaining core business functionality. More often than not, this approach is chosen when existing applications are too outdated to be efficiently modified.
Benefits:
- Customized solutions tailored to business needs
- Utilization of advanced technology stacks
- Improved system performance and user experience
6. Replace
In some cases, it is more beneficial to completely replace an existing application with a new off-the-shelf or custom-built solution that better meets business requirements.
Benefits:
- Access to modern software solutions
- Elimination of legacy system limitations
- Reduced long-term operational costs
7. Retire
If an application no longer serves a critical business function, retiring it can free up resources and reduce maintenance costs. This approach involves decommissioning obsolete systems and migrating essential data to newer platforms.
Benefits:
- Cost savings by eliminating redundant applications
- Reduced complexity in IT environments
- Improved focus on high-priority applications
Implementing a Successful Application Modernization Strategy
To ensure a smooth transition from legacy systems to modern architectures, businesses must follow a strategic approach. Here’s a step-by-step guide to implementing an Application Modernization Strategy:
Step 1: Assess Legacy Systems
Evaluate existing applications to determine their limitations, performance bottlenecks, and compatibility with modern technologies.
Step 2: Identify Business Needs
Align modernization efforts with business objectives, customer expectations, and industry trends.
Step 3: Choose the Right Modernization Approach
Based on the assessment, select the most suitable approach from the 7 R’s of Application Modernization.
Step 4: Develop a Migration Plan
Create a roadmap outlining timelines, resource allocation, risk mitigation, and cost estimation for the modernization process.
Step 5: Execute the Modernization Strategy
Implement the chosen modernization strategy with minimal disruption to business operations.
Step 6: Monitor and Optimize Performance
Continuously track application performance, gather user feedback, and make iterative improvements to enhance efficiency.
Step 7: Future-Proof Applications
Application modernization is an ongoing process. Therefore, businesses should regularly revisit applications to ensure they remain aligned with evolving business and technological landscapes.
Future-Proof Your Business with Athena Global Technologies
As businesses embrace digital transformation, a well-executed Application Modernization Strategy is key to maintaining competitiveness, efficiency, and innovation. Whether it’s rehosting, refactoring, or replacing legacy systems, adopting the right Application Modernization Strategies ensures sustainable growth and technological resilience.
With over 30 years of expertise in IT operations and management consulting, Athena Global Technologies (AGT) is the ideal partner for MSMEs and niche businesses seeking expert guidance in Legacy Application Modernization. By leveraging AGT’s expertise, businesses can unlock new opportunities, enhance security, and optimize costs while seamlessly transitioning to modern, agile systems.
Ultimately, embracing application modernization is not just about upgrading technology—it’s about securing your organization’s future in a digital-first world.


